The buildings are becoming smarter thanks to IoT, Sensors and Artificial Intelligence. These technologies provide new possibilities to assist users simplify their lives.
As a result of the ever-growing need for accessibility and flexibility, as well as user-friendly Sensor/Actuator Networks using radio or cable are becoming increasingly crucial, not only in relation in energy conservation and security of IT in the building.
KNX has become the standard worldwide for automation and communication within buildings for years. The source of the idea can be traced back around 90 under the name EIB (European Installation Bus).
After a merger with other standards such as BATIBUS (France) as well as European Home System Association (the Netherlands), the KNX association was formed in the year 2006.
Thanks to KNX an uncentralized system of bus and each of the KNX certified products from different manufacturers and providers are able to be networked and synchronized to work together.

A software tool for engineering (ETS) is used to aid in the design, configuration , and the diagnosis of all KNX networks.
The most commonly used media at the physical level are the T/P (Twisted Pair), Ethernet (IP: Internet Protocol) and Radio Communication (KNX-RF at 868 MHz).
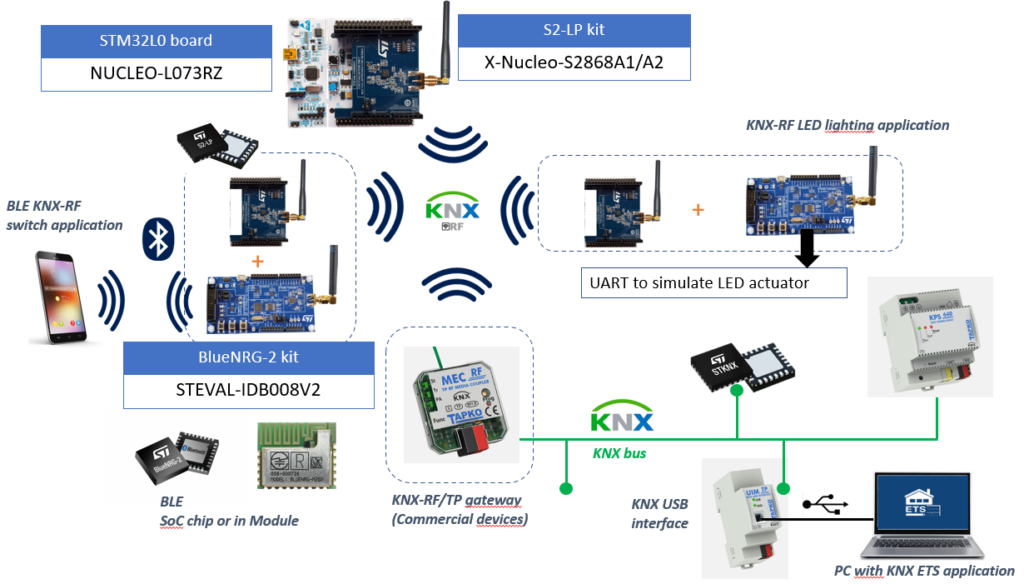
STMicroelectronics today offers the complete KNX certified chipsets for any transmission media, and also it is possible to integrate mobile devices, such as Bluetooth compatible Tablets and Smart Phones.

STKNX is an KNX Transceiver designed for Twisted Pair cables. It has two voltage regulators integrated in the KNX Bus for wired communications that today secures the biggest market share in automation for buildings.
KNX-RF is now using radio technology that operates in the 868 MHz range.
KNX devices are easily connected to the wiring infrastructure that is part of KNX by using ETS.
The chipset is able to be integrated into the implementation of a KNX-RF stack through KNX accredited partners.
TAPKO Technologies GmbH www.tapko.de already provides accredited KNX Stacks (KAIStack) to ST. ST platform.
Figure 4 illustrates the Figure 4 shows the Software Layer Integration of KNX RF and the BLE Stack into the BlueNRG-2 Host that is connected via SPI directly to SubGHz KNX-RF Transceiver.
The 32-bit Cortex M0 ARM BlueNRG SoC is therefore the host for the S2-LP and the Controller for BLE connection, e.g. with mobile devices that run IOS as well as Android.


For Bluetooth implementation, also BLE certified ST-Modules (BlueNRG-M0/M2) are available.
If no BLE functionality is required a STM32 Microcontroller can be used as Host for KNX-RF as well.
The components as well as the KNX Stacks come KNX certified and are available online at:
Conclusion
The application area for KNX certified building components is increasing by the day.
Control of lighting, room management and monitoring of the building Remote- and automated control systems for blinds, shutters and heating, ventilation, as well as air conditioning. These systems provide innovative solutions that support Smart Buildings. Smart Building.
Different sensors from ST that are based upon MEMS and Imaging Technologies are available for moving, environmental, or optical sensors for use in Building Networks.
Bluetooth Low Energy expansions within the KNX infrastructure facilitate simpler configuration and can be used to create Human Machine Interfaces operated by mobile devices.
The utilization of KNX in Buildings can also help in reducing energy use and radio communications allow modernization and retrofitting existing infrastructures without needing build new cable.
Additionally, on the issue of smart grid technologies that incorporate electronic meters for water, energy or electric power, and heat cost allocators, interfaces for the devices are possible to interface with other subGHz wireless standards like wireless M-BUS/OMS that are that are used in the modern Metering Systems.


